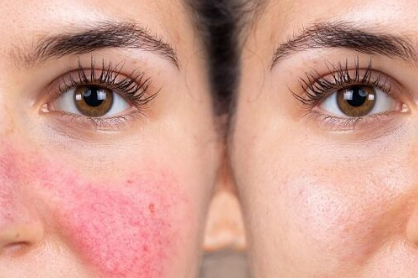
Rose disease is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition that most commonly affects the face. If rosacea is not treated, it will worsen over time. It is often confused with acne, eczema or a skin allergy.
Rose disease appears to be more common among fair-skinned people and affects 14 million people, especially in the USA. (1 out of every 20 people).
Although the causes are not fully understood and there is no cure, there are several ways to relieve symptoms.
The incidence may be much higher as it is often misdiagnosed. However, rosacea is also more common among fair-skinned people of Northern European ancestry.
Fast facts on rosacea
The main symptom of rosacea is the development of facial pustules.
Other symptoms include flushing and inflamed blood vessels.
The exact causes are unknown, but certain factors can trigger symptoms.
Certain foods, such as dairy products and spicy foods, can worsen symptoms.
Rose disease treatment
There is no cure for rosacea. However, there are several treatments that can relieve signs and symptoms.
A combination of medications and lifestyle changes often produces the best results in the face of this ailment.
Skin specialists can prescribe camouflage creams for their patients that mask blemishes on the skin.
Drugs that can be used for rosacea.
Treatment may include a combination of prescribed topical medications (applied to the skin) and oral medications (swallow pills, tablets, or capsules). These:
Topical medications: These help reduce inflammation and redness and are applied to the skin once or twice a day. They are commonly used in conjunction with some oral medications. Antibiotics (metronidazole), tretinoin, benzoyl peroxide, and azelaic acid are examples of commonly prescribed topical medications.
Oral antibiotics: These can be prescribed for their anti-inflammatory properties. Oral antibiotics tend to give results faster than topical ones. Examples include tetracycline, minocycline, and erythromycin.
Isotretinoin (Accutane): This oral medication is used for severe cases of inflammatory rosacea if other treatments have not worked. Isotretinoin is a powerful drug that inhibits oil production by the sebaceous glands. The patient should be closely monitored, as side effects can be severe.
Blefhamid : It is a specific type of steroid eye drops that is sometimes prescribed for patients with ocular rosacea (eye symptoms). Eye drops are applied daily for 3 days to 1 week, followed by a break or tapered use.
Tetracyclines: These are sometimes prescribed for patients with symptoms of ocular rosacea. Doxycycline helps improve dryness, itching, blurred vision, and photosensitivity (sensitivity to light).
laser therapy
For patients with visible blood vessels (telangiectasia), laser therapy using intense pulsed light can be used to shrink them. This will be done by a dermatologist. Although the procedure may cause some pain, most patients can tolerate it without the need for anesthesia.
Laser therapy can sometimes cause bruising, skin crusting, swelling, tenderness, and very rarely, infection. These complications usually go away within a few weeks, but may require antibiotics if they become infected.
Plastic surgery for thickened skin (Rinofima)
If the patient develops a swollen enlarged red nose and puffy cheeks and possibly thick bumps on the lower half of the nose and nearby cheek areas, they may be referred to plastic surgeons. Laser or scalpel surgery may be done to remove excess tissue and remodel the nose. A carbon dioxide laser can also be used to shrink tissue.
Types
There are many types of rosacea, according to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), but they are divided into four main types:
Erythema Telangiectatic Rose Disease has redness and redness with visible blood vessels.
Papulopustular Rose Disease includes redness, swelling, and breakouts that resemble acne.
Phymatous Rose Disease causes the skin to thicken and take on a bumpy texture.
Ocular Rose Disease causes redness and irritation of the eyes and swollen eyelids.
Causes
Experts aren’t sure what causes rosacea. The following relevant factors are thought to contribute:
Abnormalities in facial blood vessels: Skin specialists (dermatologists) suggest that abnormalities in facial blood vessels cause redness, persistent redness and visible blood vessels. What causes blood vessels to become inflamed is still a mystery.
Fair skin color: A much higher percentage of people with fair skin develop rosacea compared to other people.
Demodex folliculorum (microscopic mite): Demodex folliculorum lives on human skin and usually does not cause problems. However, the number of these mites is higher in rosacea patients than others. It is unclear whether mites cause rosacea or whether rosacea causes an overpopulation of the mites.
pylori bacteria: H. pylori, a bacterium found in the gut, stimulates the production of bradykinin, a small polypeptide known to cause dilation of blood vessels. Experts suggest that this bacterium may play a role in the development of rosacea.
Family history (heredity, genes): The aforementioned disorder is closely related to genetic inheritance in most of the patients with rosacea.
Rose disease triggers.
Certain factors can exacerbate rosacea or make it worse by increasing blood flow to the surface of the skin; these include:
extreme temperature
Sunlight, humidity or wind
Stress, anxiety, anger, shame
vigorous exercise
Hot baths or saunas
Corticosteroids and drugs used to treat high blood pressure
Acute medical conditions such as a cold, cough, or fever
Certain chronic medical conditions, such as hypertension (high blood pressure)
Foods and beverages that can trigger rosacea include:
Hot food and drinks
Caffeine
Dairy products
Spices containing capsaicin, such as hot sauce, cayenne pepper and paprika
Spirits with wines and hard liquors
Foods containing cinnamaldehyde, such as tomatoes, chocolate, and citrus fruits
Symptoms
Many signs and symptoms are associated with rosacea, but these symptoms can vary significantly from person to person.
The following signs and symptoms occur in most cases:
Washing (easily blushing): Washing sections may take up to 5 minutes. The blush may spread from the face down to the neck and chest. Some patients say that their skin feels unpleasantly hot during the rash.
Facial skin hyper-reactivity: Sensitive blood vessels expand easily to contact and other physical stimuli such as sunlight. Many mistakenly refer to it as “sensitive skin,” but with rosacea, it is caused by sensitive blood vessels and sensitive skin cells.
Permanent redness: Sometimes, continuous facial redness may appear at the end of flushing events. The redness can be long-lasting, like a sunburn patch. This occurs due to the dilation (widening) of hundreds of small blood vessels near the surface of the facial skin.
Pimples, papules and pustules (Inflammatory rose disease): Sometimes, small spots, papules and pustules are seen on the patient’s face, this is also known as inflammatory rose disease. Misdiagnosis is common due to its similarities to teen acne. However, in rose disease, black spots do not occur on the skin, unlike acne.
Inflamed blood vessels (vascular rosacea): As the signs and symptoms of rosacea progress and worsen, small blood vessels in the nose and cheeks swell and become visible (telangiectasia). This sometimes causes them to look like small spider webs.
Rhinophy or enlarged nose: Severe rosacea can cause thickening of the facial skin, especially around the skin. The nose is bulbous and may grow (rhinophyma). This is a very rare complication and tends to affect men much more than women.
Ocular rosacea: The inside of the eyelid may become inflamed (blepharitis) and may appear scaly and cause conjunctivitis. Some people may not tolerate contact lenses and may develop sties. In very rare cases, vision may become blurred. In general, blood and burning may be felt in the eyes.
Facial swelling: Excess fluid and proteins leak out of the blood vessels and eventually suffocate the lymphatic system, which cannot drain the leak fast enough. This causes fluid to accumulate in the facial skin.
natural remedies
These lifestyle and natural measures will help control symptoms and can be used in conjunction with any medical treatment.
The key here is to minimize exposure to anything that can trigger or exacerbate symptoms:
When exposed to the sun, use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 15.
In winter, protect the face with a scarf or ski mask.
Avoid touching or touching your face.
While washing, apply a mild cleanser to problem areas.
Do not use any facial products that contain skin irritants or alcohol.
Use a moisturizer if your skin is extremely dry.
Apply moisturizers only after the topical medication has dried.
Use only products labeled as non-comedogenic. These do not block the oil and sweat gland openings.
Don’t get too hot.
Avoid consuming alcoholic beverages.
An electric shaver is less likely to trigger a burn than regular shavers.
Avoid spicy foods.
Create a list of possible foods and drinks that could trigger an outbreak and avoid them.
Avoid over-the-counter (OTC) steroid creams unless your doctor has included them as part of your treatment. They can worsen symptoms in the medium or long term.
Stress
Experts say that stress is an important trigger of rosacea. Any action you take to reduce stress levels will help prevent flare-ups and existing symptoms from getting worse.
Steps to reduce stress include regular exercise, at least 7 hours of quality sleep each night, and a healthy and balanced meal schedule.
Since vigorous exercise is often a trigger, rosacea patients are advised to do low-intensity exercise such as walking or swimming.
Yoga, tai-chi, breathing exercises, and some meditations can also help reduce stress.
Diagnosis
There is no clinical test for rosacea. A doctor arrives at the diagnosis after examining a patient’s skin and asking about symptoms and triggers. The presence of enlarged blood vessels will help the doctor distinguish it from other skin disorders.
The presence of a rash on the scalp or ears usually indicates a different or existing diagnosis. The signs and symptoms of rosacea are mainly in the facial area.
Early diagnosis and subsequent prompt treatment significantly reduce the risk of progression of rosacea. If the doctor suspects that you may have an underlying medical condition or disease, such as lupus, blood tests may be ordered. The doctor may refer the patient to a dermatologist.
Complications
Some complications can occur with rosacea.
Ocular Rose Disease
If rosacea affects the eyes, the eyelids may become inflamed (blepharitis). Treatment includes daily application of topical antibiotic creams and oral antibiotics.
Self-Esteem, Shame, and Disappointment
Although rosacea is not a life-threatening condition, its effect on appearance often leaves the patient embarrassed, disappointed, anxious, and insecure.
Patients who are well informed about rosacea tend to cope better because they are prepared to deal with complications or relapses.
Emotional health usually improves when symptoms are successfully resolved. This is more likely if individuals adhere to long-term medical treatment and take measures to minimize aggravating factors.
It is important for individuals to speak to a doctor if they experience intense feelings of distress, embarrassment or frustration. Talking to a counselor or medical social worker is also recommended.
Why and how does rose disease occur?
The cause of rosacea is unknown, but it can be caused by an overactive immune system, heredity, environmental factors, or a combination of these. Rosacea is not caused by poor hygiene and is not contagious.
Exacerbations can be triggered by:
Hot drinks and spicy foods
Red wine and other alcoholic beverages
extreme temperatures
sun or wind
feelings
To exercise
Medicines that dilate blood vessels, including some blood pressure medicines
Some cosmetics, skin or hair care products






Yorumlar kapalı.